What Are The Most Common Causes Of Cellulitis?
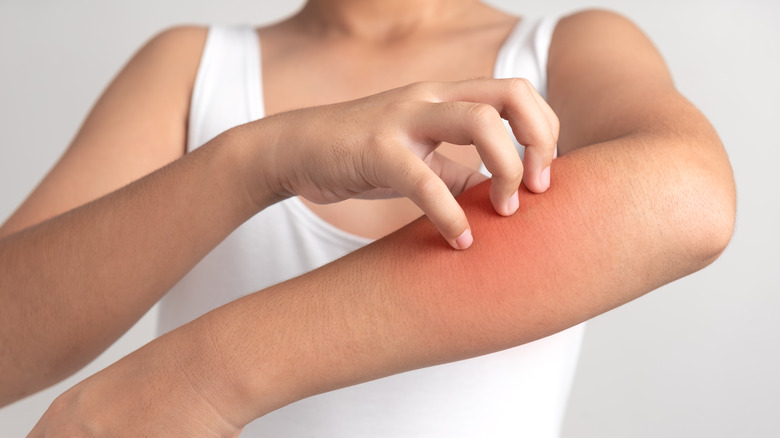
Cellulitis is a condition that affects the inside of the skin's underlying tissues, per the National Health Service (NHS). The condition affects over 14 million Americans yearly, according to a 2022 article published in Stat Pearls. It can be characterized by a number of symptoms in the affected area, and they usually develop quickly, per the Mayo Clinic. In fact, common symptoms of cellulitis include a red, swollen, and painful area of skin that is warm when touched, as well as a fever and chills, among others.
In severe cases of cellulitis or if the condition worsens or spreads in the patient, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure close monitoring and prompt treatment. If left untreated, cellulitis can lead to more serious complications, such as sepsis, which is an infection of the bloodstream which can spread to other parts of the body, as per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Therefore, taking steps to prevent cellulitis and seeking medical treatment can help reduce the risk of serious complications and ensure a full recovery (via NHS).
The causes of cellulitis
The most common causes of cellulitis are due to Streptococcus and Staphylococcus bacteria, according to the Mayo Clinic. The bacteria enters the skin through a break in the skin's barrier, such as a cut, puncture, or open wound. This can occur in healthy individuals, but those with weakened immune systems and conditions, such as diabetes, are more susceptible to developing cellulitis.
On top of that, individuals with skin conditions that cause cracked or dry skin, such as eczema athlete's foot, and shingles, are at an increased risk for cellulitis. This is because the cracks in the skin are potential entry points for bacteria and leave the skin more susceptible to infection. Additionally, those with intravenous drug use can also be at high risk of being affected with cellulitis by providing a pathway for bacteria to enter the skin, according to the Sepsis Alliance. Luckily, treatment can be done.
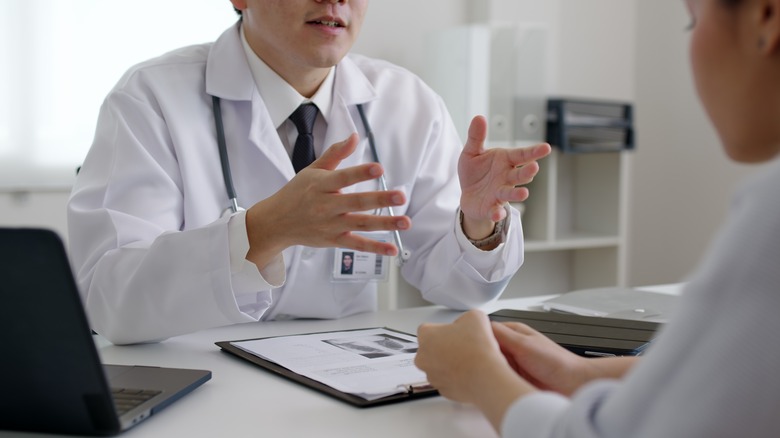
How is cellulitis diagnosed and treated?
Diagnosis of cellulitis typically involves a physical examination of the affected area and a review of the patient's medical history. This may include a skin or blood test or a bacterial culture test from the affected area to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection, per the Cleveland Clinic. Once a diagnosis of cellulitis is confirmed, treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics. In addition to antibiotics, over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
While oral antibiotics may be sufficient in mild cases, more severe cases may require intravenous antibiotics in a hospital setting to ensure close monitoring of the patient's condition and provide prompt treatment if the infection worsens or spreads.
In addition to antibiotics, taking steps to prevent cellulitis from recurring is necessary. This may include proper wound care and treatment of underlying conditions, such as eczema, regular hand washing, and avoiding close contact with individuals who have skin infections.