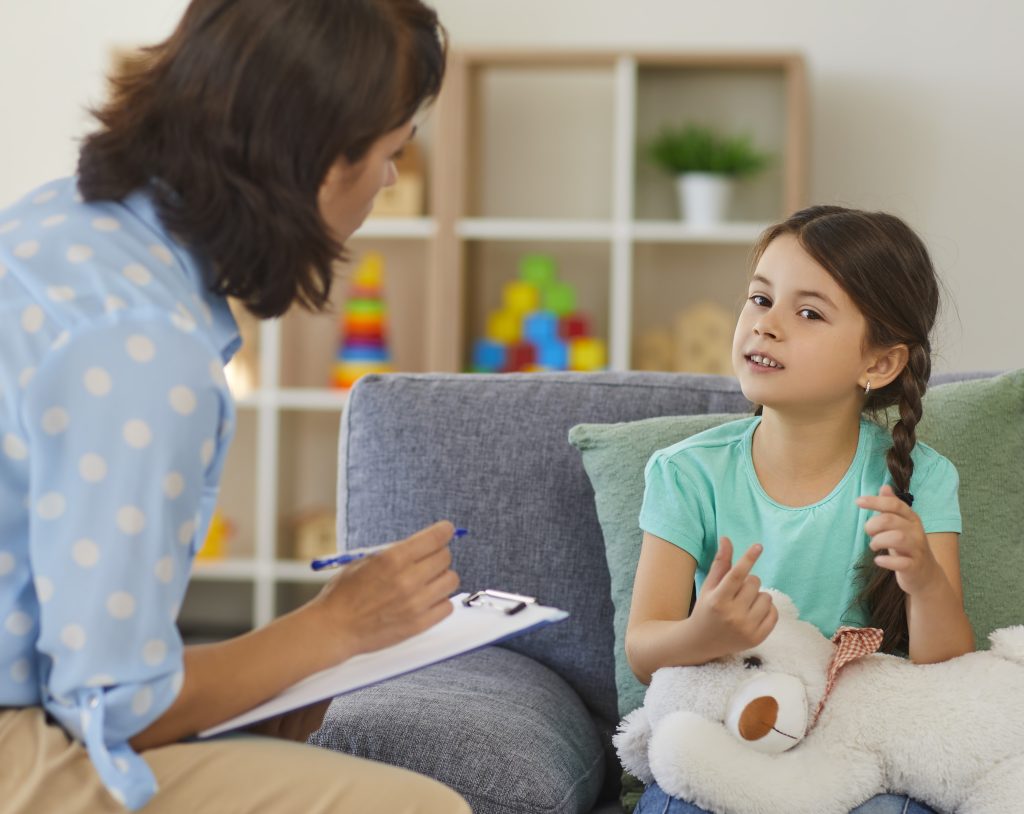
Pennsylvania faces a shortage of psychiatrists that children’s advocates call “alarming,” and they’re concerned about the impact it might have on young people whose needs become more intense and could require medication.
A June 2020 report found there aren’t enough psychiatrists to meet the demand for mental-health assistance in the Commonwealth. Pittsburgh-based psychologist Dan Warner said this means the responsibility of prescribing medication for children with severe mental-health challenges often falls on pediatricians. He said the first step should be talking to a mental-health professional.
“Under significant stress, there might be a need to elevate and really looking at a biomedical intervention,” he said. “Very often, the first line of that is starting with your pediatrician. Those people are not specially trained in the needs of children with mental health issues, and they don’t necessarily have the time to do all the kind of work.”
The most recent Pennsylvania Youth Survey found 38% of students reported feeling sad or depressed most days.
One possible solution getting the support of some health professionals is Senate Bill 25. It would allow certain nurse practitioners to have full authority to prescribe medication without requiring them to have a collaborative agreement with a physician.
State Sen. Camera Bartolotta, R-Greene County, who introduced the bill, said it would assist communities hit hardest by the shortage, both rural and urban.
“It’s very specific,” she said. “It would be highly regulated, but it would open the doors to incredibly good health care that is needed right now more than ever, especially mental health care. We’ve got hundreds of qualified nurse practitioners that could easily jump into that field and fill the void.”
Senate Bill 25 would require a qualified nurse practitioner to have 3,600 hours and three years under a physician’s collaborative agreement. The bill passed out of committee in recent months and awaits a vote in the full Senate. According to Bartolotta, it has bipartisan support.